Security Misconfiguration in WordPress (Full Guide with Code)
If attackers love anything, it’s Security Misconfiguration in WordPress—default settings left on, sensitive files exposed, permissive headers, debug switched on in production, and weak file permissions. The good news? With a few surgical tweaks, you can harden your site quickly and measurably.

Below you’ll find seven high-impact fixes (with copy-paste code for Apache, Nginx, and PHP) to eliminate the most common security misconfig issues.
Why “Security Misconfiguration in WordPress” Happens
- Default or unsafe settings (e.g., directory listing, exposed
wp-config.php) - Overly permissive file permissions/ownership
- Debug settings leaking stack traces
- Missing HTTP security headers and CSP
- Dangerous endpoints left open (XML-RPC, user enumeration via REST)
- Admin access over plain HTTP, not HTTPS
- Out-of-date core, plugins, or themes
The fixes below target these root causes of Security Misconfiguration in WordPress while keeping performance and compatibility in mind.
Fix 1: Harden wp-config.php (and Keep It Private)
Your configuration file is a treasure map. Protect it and enforce production-safe constants.
PHP (wp-config.php)
<?php
// Production-safe defaults
define('WP_DEBUG', false);
define('WP_DEBUG_LOG', false);
define('WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY', false);
// Disallow file editing in the dashboard (prevents rogue edits)
define('DISALLOW_FILE_EDIT', true);
// Force HTTPS in admin
define('FORCE_SSL_ADMIN', true);
// Explicit environment flag (WP 5.5+)
define('WP_ENVIRONMENT_TYPE', 'production');
// Optional: Move wp-content directory (advanced setups)
// define('WP_CONTENT_DIR', '/var/www/example.com/content');
// define('WP_CONTENT_URL', 'https://example.com/content');Apache (.htaccess) – protect wp-config.php
# Block direct access to wp-config.php
<Files wp-config.php>
Require all denied
</Files>Nginx – protect wp-config.php
location ~* wp-config\.php {
deny all;
}Why it matters: Prevents direct reads of secrets and reduces the blast radius of Security Misconfiguration.
Quick tip: before and after you harden anything, run a free external scan to catch misconfigurations you might miss manually.
Below is the screenshot of a Free Website Vulnerability Scanner tool page
Fix 2: Correct File Ownership & Permissions
Loose perms are a classic Security Misconfiguration. Start here:
Bash (run on the server)
# Set correct ownership (web user varies: www-data, nginx, apache)
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/example.com
# Secure directories (755) and files (644)
find /var/www/example.com -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
find /var/www/example.com -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;
# Extra-hardening for sensitive files
chmod 600 /var/www/example.com/wp-config.phpPro tip: Only grant write permissions to folders that truly need it (e.g., wp-content/uploads).
Fix 3: Kill Dangerous Endpoints (XML-RPC) & Limit REST Enumeration
XML-RPC is still exploited for brute force and DDoS amplification attacks. If you don’t need it, block it.
Apache (.htaccess)
# Block XML-RPC entirely
<Files "xmlrpc.php">
Require all denied
</Files>Nginx
location = /xmlrpc.php {
deny all;
}PHP (theme/plugin) – disable XML-RPC programmatically
add_filter('xmlrpc_enabled', '__return_false');Now, reduce REST API user enumeration—another quiet Security Misconfiguration in WordPress.
PHP (must-use plugin or theme’s functions.php)
// Block unauthenticated access to /wp/v2/users to prevent user enumeration
add_filter('rest_endpoints', function ($endpoints) {
if (isset($endpoints['/wp/v2/users'])) {
foreach ($endpoints['/wp/v2/users'] as $i => $endpoint) {
if (empty($endpoint['permission_callback'])) {
$endpoints['/wp/v2/users'][$i]['permission_callback'] = function() {
return current_user_can('list_users');
};
}
}
}
return $endpoints;
});Fix 4: Add Security Headers (and a Starter CSP)
Missing headers are a textbook for Security Misconfiguration in WordPress. Start with these:
Apache (.htaccess)
# Clickjacking protection
Header always set X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN"
# MIME sniffing protection
Header always set X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff"
# XSS Auditor legacy off; modern CSP recommended
Header always set X-XSS-Protection "0"
# Referrer privacy
Header always set Referrer-Policy "no-referrer-when-downgrade"
# HSTS (enable ONLY after HTTPS is solid; preload optional)
Header always set Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains"
# Basic Permissions Policy (restrict powerful features)
Header always set Permissions-Policy "geolocation=(), microphone=(), camera=()"Nginx
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
add_header X-XSS-Protection "0" always;
add_header Referrer-Policy "no-referrer-when-downgrade" always;
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains" always;
add_header Permissions-Policy "geolocation=(), microphone=(), camera=()" always;Starter Content Security Policy (tune per theme/plugins)
Start permissive, then tighten to minimize breakage.
Apache
Header always set Content-Security-Policy "default-src 'self'; img-src 'self' data: https:; script-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' https://cdn.jsdelivr.net https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com; style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' https://fonts.googleapis.com https://cdn.jsdelivr.net; font-src 'self' https://fonts.gstatic.com data:; connect-src 'self'; frame-ancestors 'self'; base-uri 'self'; form-action 'self'"Nginx
add_header Content-Security-Policy "default-src 'self'; img-src 'self' data: https:; script-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' https://cdn.jsdelivr.net https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com; style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' https://fonts.googleapis.com https://cdn.jsdelivr.net; font-src 'self' https://fonts.gstatic.com data:; connect-src 'self'; frame-ancestors 'self'; base-uri 'self'; form-action 'self'" always;This dramatically reduces XSS and clickjacking risks tied to Security Misconfiguration.
Fix 5: Hide Version Leakage & Block Author Enumeration
PHP (functions.php)
// Remove WP version from head and feeds
remove_action('wp_head', 'wp_generator');
// Block ?author=1 style enumeration
add_action('init', function () {
if (is_admin()) return;
if (isset($_GET['author'])) {
wp_redirect(home_url(), 301);
exit;
}
});Apache (.htaccess) – block dotfiles & VCS leaks
# No dotfiles, env files, composer, etc.
<FilesMatch "^(\.git|\.env|composer\.(json|lock)|readme\.html|license\.txt)">
Require all denied
</FilesMatch>
# Disable directory listing
Options -IndexesHiding noisy metadata chips away at Security Misconfiguration in WordPress that assists recon and automated exploits.
Fix 6: Stop Debug & Error Leaks in Production
PHP (wp-config.php)
define('WP_DEBUG', false);
define('WP_DEBUG_LOG', false);
define('WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY', false);
// If PHP ini is accessible:
@ini_set('display_errors', '0');
@ini_set('log_errors', '1');Apache / Nginx (PHP-FPM via php.ini)
display_errors = Off
log_errors = OnLeaking stack traces (paths, queries, keys) is a subtle but serious Security Misconfiguration in WordPress.
Fix 7: Updates, Least Privilege, and Backups (with CLI)
WP-CLI (where available)
# Update core, plugins, themes
wp core update
wp plugin update --all
wp theme update --all
# List outdated items
wp plugin list --update=available
wp theme list --update=available
# Create a least-privileged editor (no admin for content folks)
wp user create editor.jane [email protected] --role=editorMySQL – ensure separate DB user with least privilege
-- Example: grant only necessary privileges (adjust database/user)
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE, ALTER, INDEX
ON wp_database.* TO 'wp_leastpriv'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'STRONG_PASSWORD_HERE';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Regular updates and minimal privileges cut off broad classes of Security Misconfiguration in WordPress.
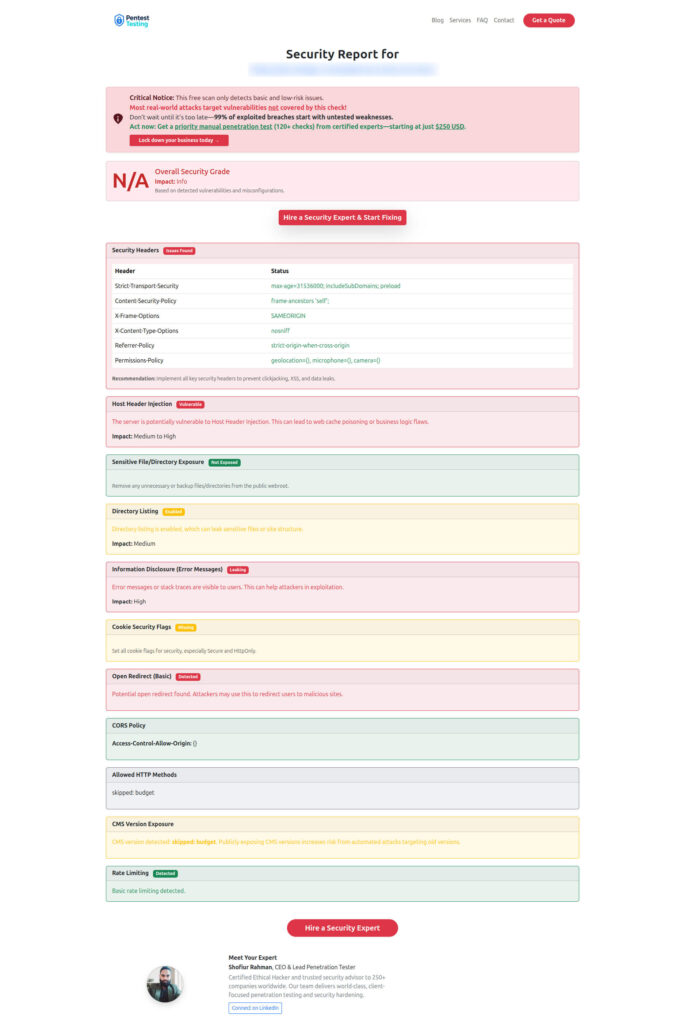
Demo: Run a Free External Scan to check Website Vulnerability
Kick the tires with our Free Website Security Scanner and watch for missing headers, open endpoints, and other misconfigurations.
Practical Snippets You Can Paste Today
Block direct access to /wp-content/uploads/*.php
Apache
# Disable PHP execution in uploads
<Directory "/var/www/example.com/wp-content/uploads">
<FilesMatch "\.php$">
Require all denied
</FilesMatch>
</Directory>Nginx
location ~* /wp-content/uploads/.*\.php$ {
deny all;
}Force HTTPS site-wide (Apache)
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} !=on
RewriteRule ^ https://%{HTTP_HOST}%{REQUEST_URI} [R=301,L]Disable XML-RPC pingbacks only (if you keep XML-RPC)
add_filter('xmlrpc_methods', function ($methods) {
unset($methods['pingback.ping']);
return $methods;
});These patterns remove low-hanging fruit responsible for Security Misconfiguration in WordPress without breaking legitimate traffic.
Further Reading (Related Posts)
Deepen your hardening beyond Security Misconfiguration with these guides:
- React: Stop Session Replay Attack in React.js
- Laravel: Stop Session Replay Attack in Laravel
- Laravel: Preventing Broken Authentication in Laravel
- WordPress: Fix Broken Access Control in WordPress
- WordPress: Fix Sensitive Data Exposure in WordPress
Managed Help & Services (Choose What Fits)
Managed IT Services for Secure Ops
If you’d rather not babysit updates, backups, and monitoring, our team can run it end-to-end. Explore our Managed IT Services to reduce downtime and misconfig risks.
AI Application Cybersecurity
Ship AI features with confidence. We secure prompts, tokens, model endpoints, and data flows. Learn more at AI Application Cybersecurity.
Offer Cybersecurity to Your Clients (White-Label)
Agencies: add pentesting and hardening under your brand. See Offer Cybersecurity Service to Your Client.
Final Checklist (Copy & Keep)
wp-config.phpprotected + production constants set- Directory listing off; dotfiles/VCS blocked
- XML-RPC disabled (or pingbacks disabled)
- REST user enumeration restricted
- Security headers + starter CSP in place
- File perms: dirs 755, files 644,
wp-config.php600 - HTTPS forced; HSTS after confirming TLS
- Least privilege DB user + role hygiene
- WP core/plugins/themes up-to-date
🔐 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Find answers to commonly asked questions about Security Misconfiguration in WordPress.


Pingback: 10 Best Fixes for Weak API Authentication in React.js