Case Study: Rapid Incident Response for a Japanese Healthcare Website
At a glance
- Industry: Healthcare
- Trigger: Malicious code injected via a third-party plugin
- Exposure: No patient data exposed (verified during triage)
- Time to restore: Same business day (site back to a secure, operational state)
- Post-incident posture: Ongoing monitoring, automated updates, WAF, and staff training

The situation: Healthcare Plugin Exploit
A Japanese healthcare provider detected suspicious behavior on its public website. Investigation revealed that a vulnerable third-party plugin had been exploited to inject malicious code. Our incident response (IR) team was engaged to contain, eradicate, and harden—while ensuring clinical services and patient communication remained uninterrupted.
Objectives
- Stop the attack and remove persistence mechanisms
- Patch known CVEs and upgrade affected components
- Harden the platform to reduce future risk
- Restore confidence with continuous monitoring and simple, repeatable processes
What we did (step-by-step)
1) Containment & forensic triage
- Placed the site in a controlled state (maintenance + selective IP allowlisting).
- Captured volatile data (process lists, crontab, web server connections) and full filesystem snapshots for later review.
- Identified common web-shell indicators and backdoors in upload directories, modified JS assets, and suspicious scheduled tasks.
- Verified no PHI/PII exfiltration using access logs, DB logs, and egress checks.
2) Eradication: clean the infection and kill persistence
- Removed injected code, rogue admin users, malicious cron jobs, dropped web-shells, and DB-level triggers.
- Rotated credentials and salts; regenerated API keys and session secrets.
3) Patch & update
- Upgraded the vulnerable plugin and core CMS components to vendor-supported versions.
- Patched all known CVEs in the web stack (runtime, libraries, and server packages).
- Implemented safer defaults for plugin/theme management (only trusted, minimal set; signed updates).
4) Hardening
- Locked down file permissions, disabled PHP execution in upload directories, and enforced least-privilege for service accounts.
- Added a Web Application Firewall (WAF) with virtual patching rules for common exploit paths and bot throttling.
- Configured strict HTTP security headers (HSTS, CSP, XFO, X-Content-Type-Options, Referrer-Policy) and rate limiting on auth endpoints.
- Removed unused plugins/themes and legacy code paths to reduce attack surface.
5) Monitoring & maintenance
- Enabled continuous uptime/integrity monitoring and anomaly alerts.
- Set automated update windows for core and approved plugins, with rollback checkpoints.
- Added a lightweight weekly security review checklist for the internal team.
6) People & process
- Delivered a 1-hour, non-technical workshop for staff: secure updates, plugin hygiene, incident checklists, and when to escalate.
- Provided a simple “break-glass” runbook for any future web compromise.
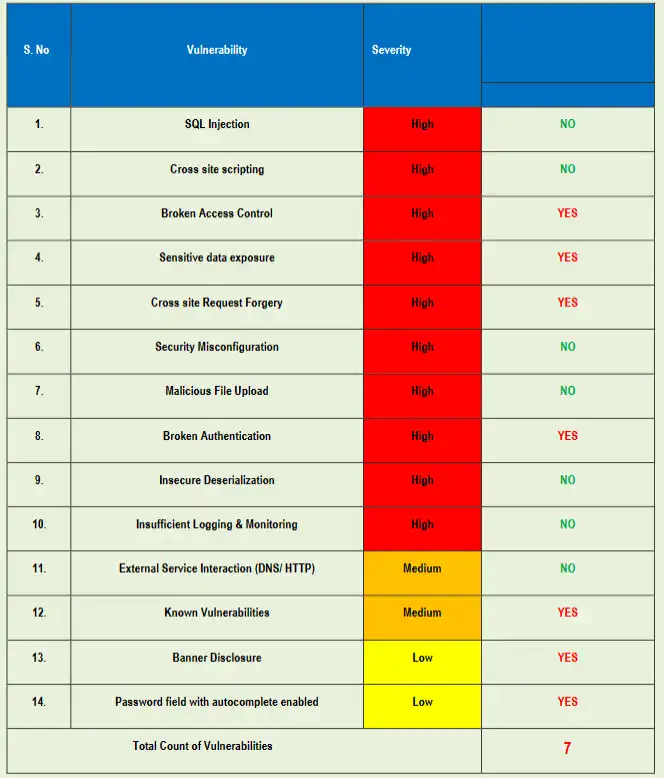
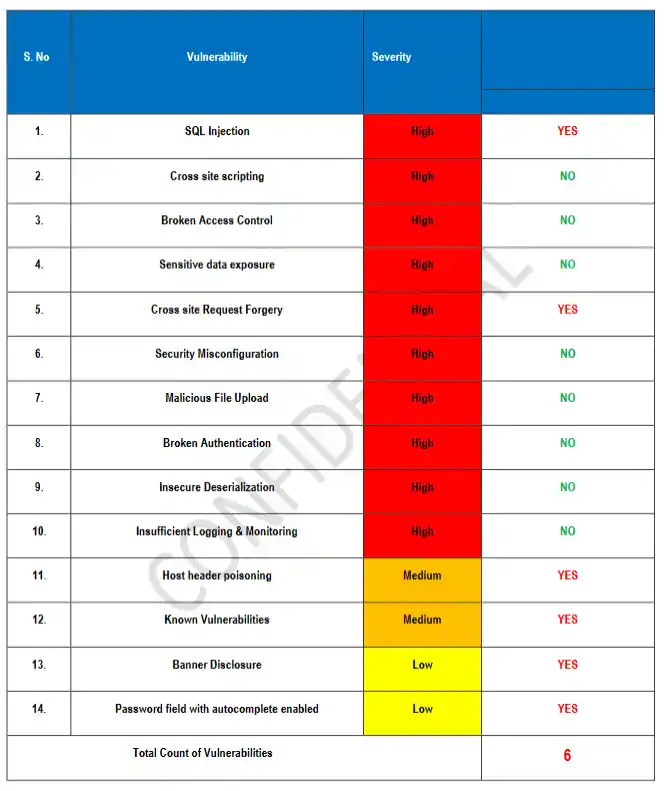
Outcome
- Service continuity maintained during remediation.
- No patient data exposed, confirmed by log/DB review and egress analysis.
- Site returned to a known-good, hardened state with monitoring and clear maintenance SOPs.
Timeline (condensed)
- Hour 0–1: Containment, forensic capture, initial indicators of compromise (IoCs) cataloged
- Hours 1–4: Malware & backdoor removal; credentials rotation; WAF rules activated
- Hours 4–8: Patch/upgrade cycle, hardening, header & rate-limit policies, validation checks
- Day 2: Post-fix verification, staff training, monitoring tuned, and final IR report delivered
Tools & techniques
- Log and integrity analysis, web-root diffing, DB trigger review, network egress validation, configuration baselining, HTTP header hardening, and WAF virtual patching.
Related services & resources
- Partner with us (white-label/referral): If you’re an agency/MSP, you can resell our audits or refer projects and earn commissions.
↳ Offer Cybersecurity Services to Your Clients - AI Application Cybersecurity: For orgs increasingly relying on ML/AI features, we assess model, data, and API risks (poisoning, extraction, prompt injection, etc.).
↳ Cybersecurity for AI Application - Free 10-point website scan: Get quick, no-pressure visibility into high-impact issues before they become incidents.
↳ Free Website Vulnerability Scanner
Our Free Website Vulnerability Scanner tool Webpage
Recommended reading (recent posts)
- Broken Authentication in WordPress: 11 Proven Fixes — practical steps, headers, 2FA, rate limiting, and more (published 5 days ago).
- Fix IDOR Vulnerability in WordPress: 7 Effective Ways — capability checks, REST security, and access control (published 7 days ago).
- 7 Powerful Fixes for Security Misconfiguration in WordPress
- Concerned about third-party scripts and data capture? For modern frontend stacks, see our step-by-step guide to blocking replay tooling: Stop Session Replay Attack in React.js.
Need rapid, no-nonsense help—or want to pressure-test your site before something breaks? Start with a free scan, or talk to us about ongoing monitoring and hardening.
- Free Website Vulnerability Scanner
- Offer Cybersecurity Services to Your Clients
- Cybersecurity for AI Application