🚨 Top 7 Ways to Prevent XML Injection in Laravel [2025 Guide]
📌 Introduction to XML Injection in Laravel
XML Injection in Laravel is a dangerous vulnerability that occurs when untrusted XML input is parsed by an application without proper validation or sanitization. This allows attackers to inject malicious XML tags or entities into the XML data, which can result in serious consequences like data exfiltration, denial of service, or SSRF (Server-Side Request Forgery).
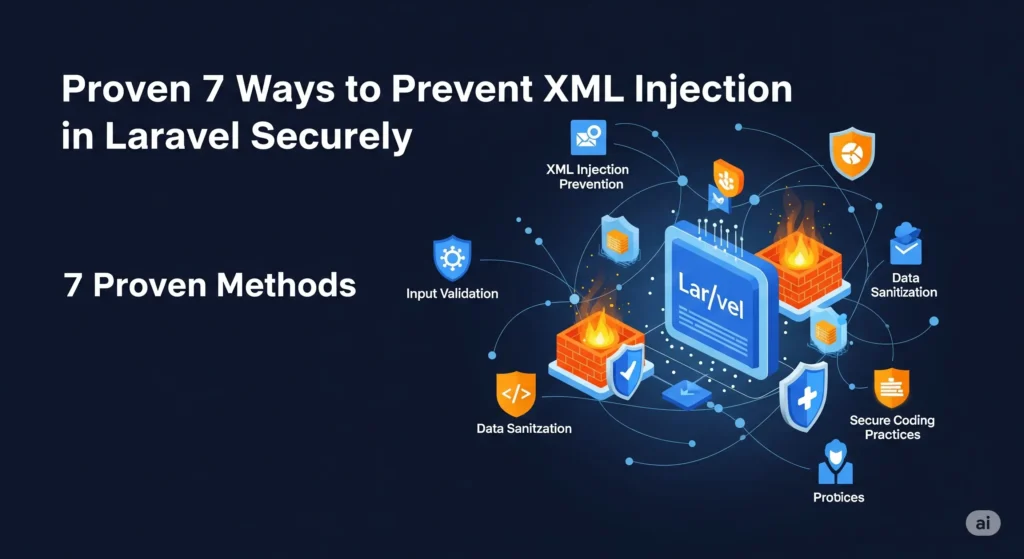
In Laravel, this typically happens when XML data is accepted from a user or external service and is parsed using PHP’s native XML libraries without disabling risky features like external entity resolution. Because XML parsing is still common in REST APIs, SOAP integrations, and config uploads, Laravel apps are often susceptible to XML Injection attacks.
💡 Why You Must Care About XML Injection
- 💥 Exploitable in XML-based APIs and SOAP integrations
- 🔓 Can lead to XML External Entity (XXE) attacks
- 📂 Sensitive file disclosure (e.g.,
/etc/passwd) - 🛑 Denial-of-Service (DoS) via entity expansion (“Billion Laughs” attack)
- 🌐 SSRF to access internal services
If you’re using DOMDocument, simplexml_load_string(), or parsing XML from third parties—you may be at risk.
🔍 Real-World XML Injection Vulnerability Scenario
Consider this basic Laravel controller that accepts XML data:
public function processXml(Request $request)
{
$xml = $request->input('xml');
$parsed = simplexml_load_string($xml); // ⚠️ Unsafe
return $parsed->user;
}Now imagine a malicious attacker submits this payload:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<!DOCTYPE foo [
<!ENTITY xxe SYSTEM "file:///etc/passwd">
]>
<user>&xxe;</user>❌ What happens?
This unsafe parser resolves the external entity, exposing sensitive server files and proving the app is vulnerable to XML Injection in Laravel.
🛡️ How to Prevent XML Injection in Laravel: 7 Secure Techniques
✅ 1. Disable External Entities (XXE) in Parsers
Prevent external entities from being parsed:
libxml_disable_entity_loader(true); // Disable globally
$dom = new \DOMDocument();
$dom->loadXML($xml, LIBXML_NOENT | LIBXML_DTDLOAD); // Avoid using NOENTWhy it works: This disables DTD processing and external entity loading—two key elements in XML Injection.
✅ 2. Use Secure Laravel Packages for XML Handling
Instead of low-level PHP functions, use secure packages:
composer require spatie/array-to-xmluse Spatie\ArrayToXml\ArrayToXml;
$data = ['user' => ['name' => 'Zubayer']];
$xml = ArrayToXml::convert($data);These libraries don’t allow unsafe parsing and offer better defaults.
✅ 3. Validate XML Input Strictly
Laravel validation should limit what comes in:
$request->validate([
'xml' => 'required|string|max:2000'
]);Never allow unbounded or deeply nested XML data.
✅ 4. Sanitize and Escape XML Content
Before parsing, sanitize using encoding:
$xml = htmlspecialchars($request->input('xml'), ENT_QUOTES | ENT_XML1, 'UTF-8');This ensures malicious characters are escaped and harmless.
✅ 5. Restrict Accepted Content-Type Headers
Only allow expected input formats:
if ($request->header('Content-Type') !== 'application/xml') {
return response()->json(['error' => 'Invalid content type.'], 415);
}✅ 6. Limit Payload Size to Prevent DoS
Set strict size limits in Laravel’s PHP config:
upload_max_filesize = 1M
post_max_size = 1MAlso handle it in your controller:
if (strlen($xml) > 2000) {
return response()->json(['error' => 'Payload too large'], 413);
}✅ 7. Detect XML Injection with Automated Tools
One of the most efficient methods is scanning for vulnerable endpoints with a tool like our Free Website Vulnerability Scanner.
📸 Our Website Vulnerability Scanner tool Interface
🧪 Advanced XML Injection Detection Logic (Laravel)
Add logging or detection logic in middleware or controller to identify suspicious input:
if (preg_match('/<!ENTITY\s+/i', $xml) || preg_match('/<!DOCTYPE/i', $xml)) {
Log::warning('Potential XML Injection Detected', ['xml' => $xml]);
return response()->json(['error' => 'Malicious XML detected'], 400);
}🛠️ Laravel Safe XML Upload with DOMDocument Example
public function uploadXML(Request $request)
{
$request->validate([
'xml' => 'required|string|max:2048'
]);
libxml_use_internal_errors(true);
libxml_disable_entity_loader(true); // Secure
$dom = new \DOMDocument();
$result = $dom->loadXML($request->input('xml'), LIBXML_NOENT | LIBXML_DTDLOAD);
if (!$result) {
return response()->json(['error' => 'Invalid XML input'], 400);
}
return response()->json(['status' => 'XML processed securely']);
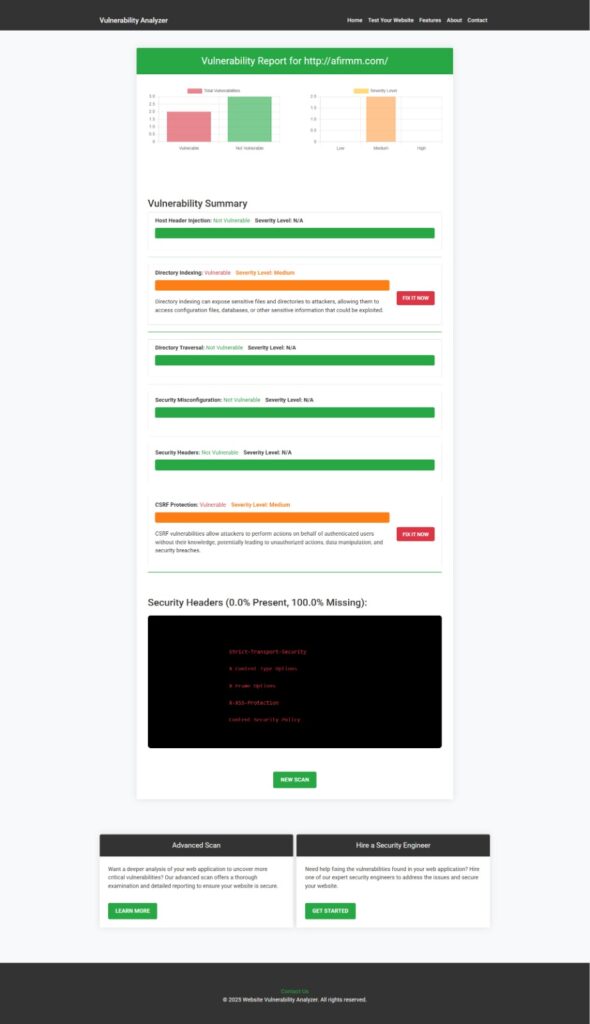
}📸 Sample Report generated by our tool to check Website Vulnerability
🔗 Related Blog Posts You’ll Love
Here are more Laravel security guides:
- 🔒 Web Cache Deception Attack in Laravel
- 🧬 Prevent NoSQL Injection in Laravel
- 🚫 How to Handle Disapproved Ads
- 🧼 HTTP Parameter Pollution in React.js
- 🚨 Stop Session Replay Attack in Laravel
🧠 Upgrade Security for AI-Powered Applications
If you’re integrating AI models or AI APIs in Laravel, ensure you’re not adding risk vectors. Learn more on our specialized AI app security page:
👉 AI Application Cybersecurity Services
🤝 Want to Resell Cybersecurity Services?
Grow your agency by offering pentesting and auditing to your clients. We offer white-label reports, lead-gen support, and direct fulfillment.
👉 Partner With Us – Cybersecurity for Your Clients
🎯 Summary: Why XML Injection in Laravel Is Critical
- XML Injection in Laravel is often overlooked yet dangerous
- Easily exploited with unsafe functions like
simplexml_load_string() - Prevention involves input validation, secure parsing, and disabling entities
- Use automation tools like ours for a Website Security test to stay safe
🚀 Want a Free Vulnerability Scan?
No registration, no hassle—scan your site instantly:
🔗 https://free.pentesttesting.com/