ASVS 5.0 Remediation: 12 Battle-Tested Fixes
Who this is for: security & engineering leaders who need real “ASVS 5.0 remediation” work done fast—and proven with artifacts auditors accept.
Quick internal links:
- Blog hub for practical how-tos and triage guides (recent posts linked below).
- Risk assessment to target the high-value fixes: https://www.pentesttesting.com/risk-assessment-services/
- Remediation services (HIPAA, PCI, SOC 2, ISO, GDPR): https://www.pentesttesting.com/remediation-services/
- Free Website Security Scanner for quick outside-in checks: https://free.pentesttesting.com/ (used throughout our blog guides).

Editor’s note — Preparing for DORA TLPT 2025? Start with our fix-first, auditor-ready playbook: DORA TLPT 2025: What to Fix First.
What changed in ASVS 5.0—and why it matters in real remediation
ASVS 5.0 (released May 2025) streamlines levels and clarifies testable controls so teams can close gaps faster with less ambiguity. It’s friendlier to remediation because each “shall” maps to concrete tests and evidence you can prove (screens, configs, logs, code diffs). We see faster hand-offs from finding → fix → verification because the level guidance is cleaner and overlaps are reduced.
Where we start: we import your open findings (ours or third-party), map each to the relevant ASVS 5.0 control and (if you’re compliance-driven) to PCI DSS 4.0/SOC 2/ISO 27001 requirements—then ship the fix plus the exact evidence artifact auditors expect.
The 12 fixes we apply most (with “before/after” code + evidence)
Below, each item includes: ASVS 5.0 area → typical finding → before code → after code → what we capture as proof.
We use multiple stacks so your team can copy/paste directly (Node/Express, Python/Flask, PHP/Laravel, Java/Spring).
Tip: Save all CLI outputs and config exports with timestamps. Tie them to the ticket that closed the finding.
1) IDOR (Broken Object Level Authorization)
ASVS 5.0: Access Control
Typical finding: GET /api/users/123 returns another user’s data when you change the ID.
Before (Express.js):
// ❌ Filters by id from the URL, no ownership check
app.get('/api/users/:id', async (req, res) => {
const user = await db.users.findById(req.params.id);
res.json(user);
});After (Express.js, server-side ownership + scoped query):
app.get('/api/me', auth, async (req, res) => {
const user = await db.users.findOne({ id: req.user.id }); // scope to caller
res.json(safeUser(user)); // no sensitive fields
});After (Laravel, policy + route model binding):
Route::get('/orders/{order}', [OrderController::class, 'show'])
->middleware('auth');
public function show(Order $order) {
$this->authorize('view', $order); // Policy enforces owner/role
return new OrderResource($order);
}Evidence: unit/integration tests showing unauthorized access fails; API gateway logs (403 on foreign IDs); code diff referencing policy/guard; screenshot of blocked request in dev tools.
2) SSRF via open URL fetches
ASVS 5.0: Server-Side Security / Network Egress
Typical finding: app fetches user-supplied URL (e.g., “fetch preview”), allowing access to metadata endpoints.
Before (Python/Flask):
# ❌ Trusts any user-provided URL
r = requests.get(request.args['url'], timeout=5)
return r.textAfter (allow-list + DNS pinning + scheme check):
from urllib.parse import urlparse
ALLOWED_HOSTS = {"api.example.com", "img.example-cdn.com"}
def safe_fetch(raw_url):
u = urlparse(raw_url)
if u.scheme not in ["https"]:
raise ValueError("Invalid scheme")
host = u.hostname
if host not in ALLOWED_HOSTS:
raise ValueError("Host not permitted")
# Optional: resolve & compare to allow-listed IPs (no private ranges)
return requests.get(u.geturl(), timeout=5, headers={"User-Agent": "SafeClient"}, allow_redirects=False)
@app.get("/preview")
def preview():
return safe_fetch(request.args["url"]).textInfra hardening (NGINX egress block for metadata):
# Block access to link-local/metadata ranges
deny 169.254.0.0/16;
deny 127.0.0.0/8;
deny 10.0.0.0/8;
deny 172.16.0.0/12;
deny 192.168.0.0/16;Evidence: tests showing private IP targets blocked; WAF/egress firewall policy export; curl attempts to 169.254.169.254 returning 403.
3) Weak session management (cookies too permissive)
ASVS 5.0: Session Management
Before (Express + cookie-session):
app.use(session({
secret: process.env.SESSION_SECRET,
cookie: { secure: false, httpOnly: false, sameSite: 'lax' } // ❌
}));After (hardened cookie):
app.use(session({
secret: process.env.SESSION_SECRET,
name: "__Host-app",
cookie: {
path: "/", secure: true, httpOnly: true, sameSite: "strict", maxAge: 15*60*1000
}
}));Evidence: Set-Cookie header screenshot (Secure; HttpOnly; SameSite=Strict; short TTL); session rotation shown in logs after privilege change.
4) Insecure JWT handling (localStorage, alg confusion, missing claims)
ASVS 5.0: Authentication / Session / Cryptography
Before (SPA using localStorage + HS/RS confusion):
// ❌ XSS steals tokens from localStorage
localStorage.setItem("jwt", token);
// ❌ Server verification without algorithm pinning
jwt.verify(token, publicKeyOrSecret);After (httpOnly cookie + strict verify):
// Server: set short-lived, httpOnly, Secure, SameSite=Strict cookie
res.cookie("__Host-id", token, {
httpOnly: true, secure: true, sameSite: "strict", path: "/", maxAge: 900000
});
const verified = jwt.verify(token, publicKey, {
algorithms: ["RS256"], // pin acceptable algs
audience: "your-app", issuer: "your-issuer"
});Evidence: browser storage shows no tokens in localStorage/sessionStorage; decoded JWT contains exp, aud, iss; verification code pins alg.
5) Output encoding gaps (XSS in templating)
ASVS 5.0: Output Encoding / Injection Prevention
Before (Jinja2):
<div>{{ user.bio | safe }}</div> <!-- ❌ -->After:
<div>{{ user.bio }}</div> <!-- auto-escaped -->Evidence: unit test rendering <script>alert(1)</script> shows literal text; CSP header export with script-src 'self'.
6) Password policy & MFA enforcement gaps
ASVS 5.0: Authentication / Credential Management
Before (Spring Security):
http.formLogin();After (Spring Security + MFA gate sample):
http
.csrf().and()
.requiresChannel(channel -> channel.anyRequest().requiresSecure())
.headers(h -> h.contentSecurityPolicy("default-src 'self'"))
.authorizeHttpRequests(auth -> auth
.requestMatchers("/mfa/**").authenticated()
.anyRequest().permitAll())
.oauth2Login(oauth -> oauth.userInfoEndpoint())
.sessionManagement(sm -> sm.sessionFixation().migrateSession());(Pair with IdP policy that enforces phishing-resistant MFA for admins.)
Evidence: IdP policy export showing enrollment & enforcement; login flow screenshots with MFA prompts.
7) CSRF protections missing on state-changing endpoints
ASVS 5.0: CSRF
Before (Flask):
@app.post("/settings")
def save_settings():
# ❌ no csrf token validationAfter (Flask-WTF CSRF):
@app.post("/settings")
@csrf.exempt # remove this; include CSRF token in form or header
def save_settings():
validate_csrf_token(request)Evidence: 403 on missing/invalid CSRF; middleware/config screenshots.
8) Insecure file upload (type/size/path traversal)
ASVS 5.0: File Handling
Before (Node):
upload.single('file'), (req,res)=>fs.writeFileSync('/uploads/'+req.file.originalname, req.file.buffer)After:
const ALLOWED = new Set(["image/png","image/jpeg","application/pdf"]);
const MAX = 5 * 1024 * 1024;
const safeName = crypto.randomUUID();
if (!ALLOWED.has(req.file.mimetype) || req.file.size > MAX) return res.status(400).end();
fs.writeFileSync(path.join(UPLOAD_DIR, safeName), req.file.buffer, { flag: 'wx' });Evidence: 400s for disallowed types; storage shows random filenames; antivirus/DLP logs.
9) Missing security headers (HSTS, CSP, Referrer-Policy)
ASVS 5.0: HTTP Security
Before (NGINX):
# noneAfter:
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload" always;
add_header Content-Security-Policy "default-src 'self'; frame-ancestors 'none'";
add_header Referrer-Policy "no-referrer";
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff";
add_header X-Frame-Options "DENY";Evidence: scanner/response headers screenshot; HSTS preload check results.
10) Encryption at rest/in transit not enforced
ASVS 5.0: Cryptography / Data Protection
Before (PostgreSQL): plaintext column
After (pgcrypto example):
ALTER TABLE customer ADD COLUMN ssn_enc bytea;
UPDATE customer SET ssn_enc = pgp_sym_encrypt(ssn, current_setting('app.key'));
ALTER TABLE customer DROP COLUMN ssn;Evidence: DDL migration + sample decrypted read in privileged context; TLS config export for DB and reverse proxy.
11) Logging sensitive data (JWTs, secrets)
ASVS 5.0: Logging
Before:
console.log("Authorization:", req.headers.authorization); // ❌ logs bearer/JWTAfter:
const redacted = (h) => h.replace(/Bearer\s+[A-Za-z0-9\.\-_]+/g, "Bearer [REDACTED]");
logger.info({ path:req.path, auth: redacted(req.headers.authorization||"") });Evidence: log samples with redaction; SIEM rule showing token patterns suppressed.
12) Insecure direct SQL (injection risk)
ASVS 5.0: Injection
Before (PHP):
$q = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE email = '".$_GET['email']."'";After (PDO prepared):
$stmt = $pdo->prepare("SELECT * FROM users WHERE email = :email");
$stmt->execute(['email' => $_GET['email']]);Evidence: code diff, test payloads fail (' OR 1=1 --); WAF rule export.
Mapping: frequent findings → ASVS 5.0 sections (quick reference)
- IDOR → Access Control
- SSRF → Server-Side Security / Egress Controls
- Weak session/JWT → Session & Authentication / Cryptography
- XSS/encoding → Output Encoding / Content Security Policy
- CSRF → CSRF Protections
- Uploads → File Handling
- Headers → HTTP Security
- Logging → Logging & Monitoring
- SQLi → Injection Prevention
2025 compliance pressure: how this ties to PCI DSS 4.0 gaps
Future-dated PCI DSS 4.0 requirements are now live (effective March 31, 2025). In practice, your ASVS 5.0 remediation stories produce the exact artifacts QSAs look for: MFA enforcement screenshots, log review automation exports, re-scan/pen-test validation, CSP/SRI configs for e-commerce, and ticket trails that prove closure. For a focused plan, see our PCI 4.0 remediation playbook—and use our free scanner for quick wins your assessor will appreciate.
Copy-ready checklist (drop into your ticket template)
- Map finding to ASVS 5.0 control and compliance tag (PCI Req, SOC 2, ISO Annex A).
- Implement code fix/config change (attach diff/commit link).
- Add/adjust tests (unit/integration/e2e) that would catch a regression.
- Update headers/policies (HSTS, CSP, cookie flags).
- Validate MFA/IdP policy for admins/support flows.
- Run authenticated internal scan and outside-in check; attach reports.
- Capture screenshots/logs/config exports with timestamps.
- Re-test and document closure (who/when/how).
- Schedule re-verification in CI and calendar (quarterly/after change).
Free Website Vulnerability Scanner — home screen
Evidence bundle template (auditor-ready)
1. Ticket & narrative
- Finding summary, risk rating, affected assets
- ASVS 5.0 control(s) + compliance mapping
2. Before/after artifacts
- Code diffs (links), config exports, policy screenshots
- Test cases proving failure before / pass after
3. Verification
- Outside-in report (headers/TLS/CMS issues) from the Free Website Security Scanner
- Authenticated scan excerpts (internal)
- Pen-test retest note with date & scope
4. Governance
- Updated SOPs/runbooks (versioned)
- Exception/risk acceptance (if any) with expiry & owner
5. Sign-off
- Control owner & security reviewer approvals
Sample scan report to check Website Vulnerability — audit-ready findings summary
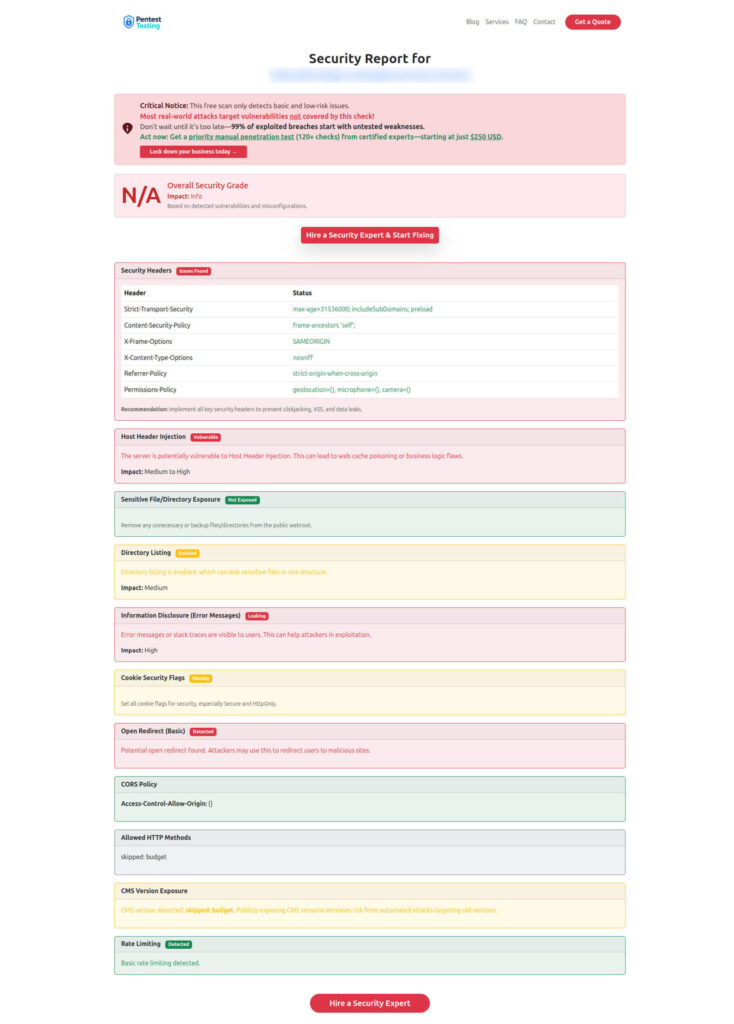
“Run a free outside-in check before your next retest: https://free.pentesttesting.com/”
Where our team fits (and how we deliver fast)
- Risk target first: we start with a concise risk review to focus fixes that collapse the most risk now. https://www.pentesttesting.com/risk-assessment-services/
- Remediate & prove: we implement code/config fixes and assemble the evidence bundle above so audits go smoothly. https://www.pentesttesting.com/remediation-services/
- Free 30-day retest: included as standard—so you ship with confidence.
- Recent, practical reads:
- VMware playbook (7 steps with copy-ready scripts).
- CISA KEV contextual prioritization (score + automate).
- Windows 10 End-of-Support remediation plan.
- PCI DSS 4.0 post-deadline remediation plan.
- 7 Proven Ways to Tame AI-Generated Code Supply-Chain Risk
If your team is seeing similar “recharge to earn” pitches, read our Oka-Furniture.com scam analysis and takedown steps: https://www.pentesttesting.com/oka-furniture-com-scam/
Explore more on our Blog: https://www.pentesttesting.com/blog/
Ready to close your ASVS 5.0 gaps?
Book a quick triage: https://www.pentesttesting.com/remediation-services/
Or email [email protected] and mention “ASVS 5.0 remediation” in the subject.
P.S. Want more hands-on playbooks? See our latest posts on the Pentest Testing Corp Blog.
🔐 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Find answers to commonly asked questions about ASVS 5.0 remediation.

