New CISA KEV: Juniper J-Web Risk & Remediation (What to fix now)
Editor’s note (1 min): There’s confusion online between CVE-2025-29829 (a Windows driver issue) and Juniper J-Web. The Juniper item actually added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) in 2025 is CVE-2025-21590 (Junos OS kernel, local code-injection after shell access). While not a J-Web bug, it’s a real KEV deadline that demands action. Meanwhile, J-Web remains a high-risk attack surface, with a fresh 2025 exposure bug (CVE-2025-6549) and the well-known 2023 pre-auth J-Web RCE chain (CVE-2023-36844/5/6/7) that’s already in KEV. Treat them together: patch, remove J-Web from the internet, and verify.

Why CVE-2025-29829 matters (risk in plain English)
- KEV means exploitation is confirmed or credible and federal agencies must remediate by CISA’s due dates under BOD 22-01; everyone else should treat KEV as a patching priority list.
- J-Web is a repeat offender: 2023’s pre-auth chain enabled file upload and environment manipulation that attackers used to achieve RCE; 2025’s CVE-2025-6549 can expose J-Web on additional interfaces, expanding attack surface if you’re not strict on management-plane isolation.
What exactly changed this year?
1) CVE-2025-21590 (KEV) — Junos OS kernel (local, but serious in real networks)
- In KEV (added Mar 2025) with required remediation under BOD 22-01. If an attacker gains shell access (e.g., via lateral movement or chained bugs), this flaw allows arbitrary code injection at the kernel boundary. Patch timelines are enforced for U.S. FCEB agencies; others should match the urgency.
2) CVE-2025-6549 — J-Web exposure on SRX (widens the blast radius)
- Incorrect authorization in the web server of Junos OS on SRX can let an unauthenticated attacker reach J-Web when it shouldn’t be reachable, depending on interface exposure. This doesn’t by itself equal RCE, but it brings attackers to the front door where past J-Web bugs delivered RCE. Patch and lock down management interfaces.
3) Historical context: 2023 J-Web pre-auth RCE chain
- CVE-2023-36844/5/6/7 enabled pre-auth code execution on EX/SRX via PHP env manipulation + upload paths; these were added to KEV with federal due dates in 2023 and continue to be probed today on internet-exposed devices. If you never fixed those or left J-Web exposed, assume compromise.
Affected devices & versions (quick view)
- CVE-2025-21590 (KEV): Junos OS kernel (see Juniper JSA for the exact version matrix and fixed trains).
- CVE-2025-6549: SRX Series Junos OS web server (J-Web)—improper authorization can expose J-Web more broadly; Juniper’s July 2025 advisory lists affected releases and fixes.
- J-Web RCE chain (2023): EX/SRX on vulnerable 22.x–23.x trains prior to specific fixed releases. If you’ve jumped multiple trains since 2023 but kept J-Web accessible from untrusted networks, review configs and update anyway.
Bottom line: If J-Web has ever been internet-facing, treat this as urgent regardless of current firmware. Patch, reduce exposure, and check for compromise indicators.
Remediation plan (do these in order)
- Upgrade firmware to Juniper’s fixed releases for both the kernel KEV (CVE-2025-21590) and J-Web exposure (CVE-2025-6549) on SRX; confirm the exact train from Juniper JSAs before scheduling.
- Remove J-Web from the internet:
- Disable J-Web entirely on internet-facing interfaces, or
- Restrict to management VRF, out-of-band networks, and allow-lists (trusted admin subnets/VPNs only). Historical guidance from 2023 RCE incidents recommended the same.
- Rotate credentials & session secrets used for web admin and automation (local accounts, TACACS/RADIUS, API tokens).
- Turn on and retain logs: HTTP daemon/J-Web, system, and config change logs. Forward to your SIEM with alerts for J-Web access attempts and admin actions (Splunk and others published analytics for Juniper RCE patterns).
- Harden the management plane:
- Enforce MFA for admin portals.
- Apply IP restrictions and rate-limits on management services.
- Use separate admin VLAN/VRF, no NAT from public.
- Network monitoring: Watch for scans and anomalous POSTs to
/jweb/paths, spikes in CPU, and unexpected PHP environment variables (a hallmark from 2023).
Verification: prove it’s fixed (for security and auditors)
- External rescan (quick):
Paste your perimeter URLs into our Website Vulnerability Scanner online free to confirm J-Web isn’t reachable externally and that patched versions present expected headers.
Screenshot of the free Website Vulnerability Scanner landing page
- Config audit (depth):
Export running config and verify: J-Web disabled or bound to mgmt VRF only; interface/zone allow-lists; admin auth policies; TLS settings; logging destinations. Keep before/after diffs and screenshots ofshow system commitentries. - Proof-of-remediation artifacts (keep these):
- Version evidence: screenshot/CLI of Junos OS version showing fixed train.
- Access-control evidence: firewall filter/policy snippets blocking J-Web from untrusted networks.
- Log evidence: SIEM screenshots showing alerts configured and benign baseline.
- Scan evidence: PDF/PNG export from your rescan (see below) attached to ticket.
These artifacts support PCI DSS, SOC 2, and ISO 27001 control narratives and audit sampling. For help packaging this, see our Risk Assessment and Remediation services.
- Follow-up rescan (evidence):
Sample “no exposure” report from our free scanner to check Website Vulnerability
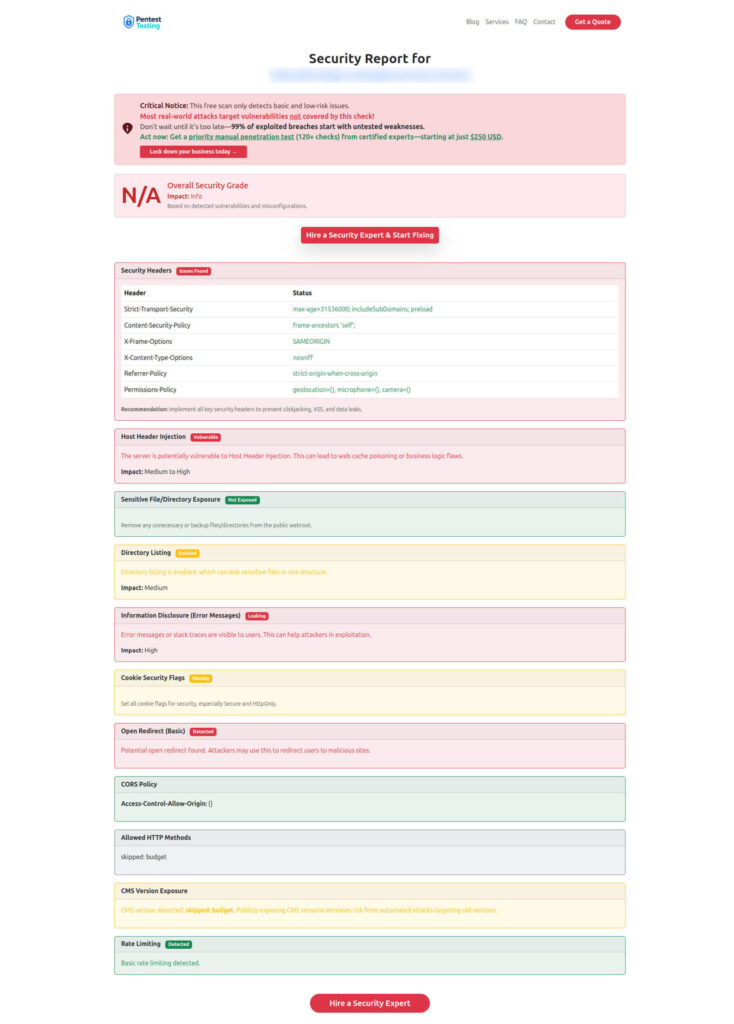
Helpful links (read this next)
- CISA KEV catalog (live due dates & entries). (CISA)
- BOD 22-01 overview (what KEV due dates mean). (CISA)
- Juniper advisory — CVE-2025-6549 (J-Web exposure). (supportportal.juniper.net)
- Juniper 2023 J-Web pre-auth RCE chain & fixes. (supportportal.juniper.net)
Where Pentest Testing Corp helps (risk & remediation focus)
- Rapid KEV Gap Review — We map your EX/SRX fleet, J-Web exposure, and patch levels; you get a prioritized plan and audit-ready artifacts.
→ Risk Assessment Services: https://www.pentesttesting.com/risk-assessment-services/ - Hands-on Remediation — We implement interface hardening, ACLs, MFA for admin, log pipelines, and version upgrades—then package proof-of-remediation.
→ Remediation Services: https://www.pentesttesting.com/remediation-services/ - Free perimeter checks — Quick external scans to ensure J-Web isn’t exposed: https://free.pentesttesting.com/
- Explore more insights on our Blog:
→ https://www.pentesttesting.com/citrix-netscaler-cve-2025-7775/ | https://www.pentesttesting.com/cisa-kev-adds-cve-2025-5086/ | https://www.pentesttesting.com/blog/ - Additional resources from our partner site (API pentesting & more):
→ https://www.cybersrely.com/ | https://www.cybersrely.com/api-penetration-testing-services/
Contact: [email protected]
Final takeaway
- Patch Junos to address CVE-2025-21590 and CVE-2025-6549.
- Eliminate J-Web exposure beyond trusted admin networks.
- Verify and document fixes with rescans, config audits, and logs for compliance.
Security teams that patch + harden + prove will pass audits and stay out of breach reports.
🔐 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Find answers to commonly asked questions about CVE-2025-29829.

