🚀 Top 7 Ways to Prevent Cache Poisoning in Laravel [With Code Examples]
Introduction: What is Cache Poisoning in Laravel?
Cache poisoning in Laravel is a critical web security flaw that can allow attackers to inject malicious content into your application’s cache. Since Laravel heavily uses caching mechanisms to improve performance, this vulnerability can lead to serving compromised content to legitimate users, affecting trust, SEO, and data integrity.

In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn:
✅ What cache poisoning in Laravel is.
✅ How attackers exploit it.
✅ 7 secure coding techniques to prevent it, with real code examples.
✅ Tools and services to assess and fix this vulnerability.
We’ll also include real-world screenshots, related helpful blogs, and a walkthrough of our website vulnerability scanner online free to help you secure your Laravel apps quickly.
What is Cache Poisoning in Laravel?
In Laravel, caching mechanisms store dynamic responses to improve application performance. But if the cache key or content is improperly validated, an attacker may send a crafted HTTP request that poisons the cache with malicious content. Later, users who access the cached content receive tampered or harmful data.
Examples of impact:
- Injecting malicious JavaScript in cached pages.
- Serving incorrect or unauthorized content.
- Downgrading security headers.
How Cache Poisoning Works:
// Insecure example
$key = 'page_' . $_GET['page'];
$content = Cache::remember($key, 60, function () {
return view('page');
});Here, $key can be controlled by the user ($_GET['page']), which enables attackers to poison the cache.
Why You Must Fix Cache Poisoning in Laravel
Not addressing this can lead to:
- SEO penalties due to malicious content served.
- Loss of user trust.
- Legal liabilities for serving harmful scripts.
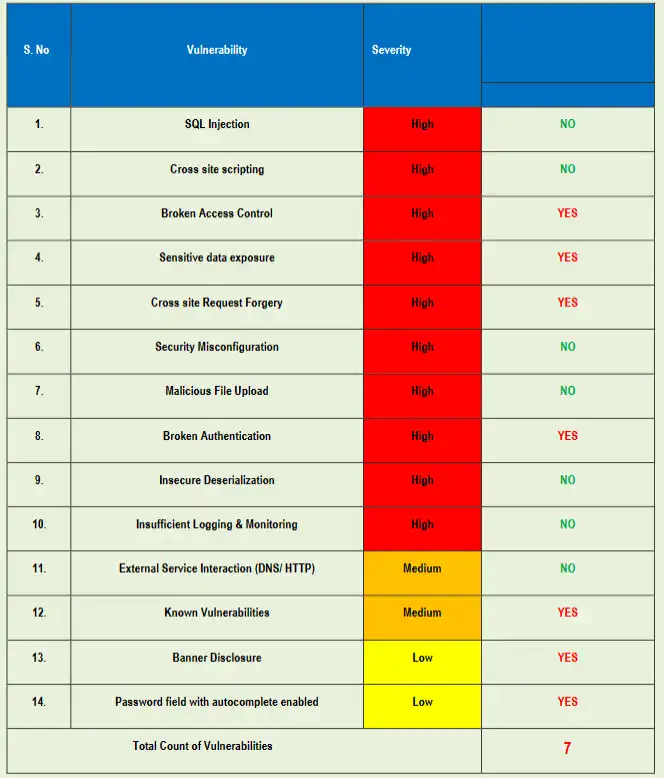
For a quick free scan of your Laravel site, use our Website Vulnerability Scanner.
📷 Screenshot of our Free Tools Page:
7 Proven Ways to Prevent Cache Poisoning in Laravel
1️⃣ Validate All User Input
Never trust raw user input when building cache keys.
✅ Secure Example:
$page = (int) request()->get('page', 1);
$key = 'page_' . $page;
$content = Cache::remember($key, 60, function () {
return view('page');
});2️⃣ Use Strong Cache Key Naming
Create predictable, validated keys:
$key = sprintf("user_%d_profile", auth()->id());3️⃣ Filter and Normalize Headers
Some attackers craft headers (X-Forwarded-Host, etc.) to influence cache. Use Laravel’s built-in request sanitization:
$request->headers->remove('X-Forwarded-Host');4️⃣ Enable HTTPS Everywhere
Mixed content over HTTP can contribute to cache poisoning attacks.
5️⃣ Set Proper Cache-Control Headers
return response($content)
->header('Cache-Control', 'no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate');6️⃣ Separate Public & Private Content
Use different cache stores for public vs private data.
Cache::store('redis')->put('public_page', $data, 60);
Cache::store('memcached')->put('user_profile_' . auth()->id(), $data, 60);7️⃣ Regularly Audit and Purge Cache
Schedule periodic cache clearing:
Artisan::call('cache:clear');Run a Vulnerability Assessment
You can run a free vulnerability assessment report of your Laravel app right now using our free tool to check the app’s vulnerability.
📷 Screenshot of Vulnerability Assessment Report:
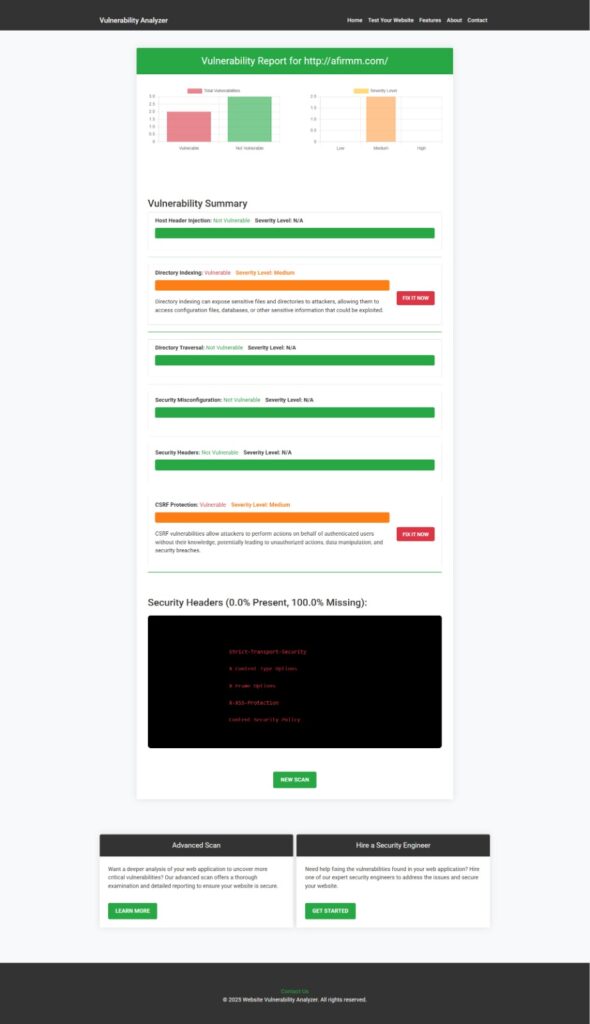
Run your scan now at 👉 https://free.pentesttesting.com/
Related Articles You Shouldn’t Miss
If you’re securing Laravel apps, also read:
- 🔗 Prevent NoSQL Injection in Laravel
- 🔗 Insecure Deserialization in Laravel
- 🔗 How to Secure OpenCart Store
- 🔗 WebSocket Vulnerabilities in Laravel
- 🔗 Fix Weak SSL/TLS Configuration in React.js
These guides complement the work you’ve done to prevent cache poisoning in Laravel.
Our Professional Services
🌐 Web App Penetration Testing Services
If you want experts to simulate real-world attacks and find vulnerabilities like cache poisoning in Laravel and others, check out our service page:
👉 Web Application Penetration Testing
🤝 Partner with Us: Offer Cybersecurity to Your Clients
If you’re an agency, hosting provider, or developer looking to offer added value to your clients:
👉 Offer Cybersecurity Services to Your Clients
Conclusion: Secure Your Laravel Apps Against Cache Poisoning
Cache poisoning in Laravel is a subtle yet dangerous threat that can compromise your web application’s integrity. With the 7 actionable techniques and code examples provided here, you’re now equipped to secure your apps better.
We also recommend you run regular vulnerability scans using our free tool for a Website Security check and consider a professional penetration test for peace of mind.